Using the sager package to import
and analyse sage results in R
Laurent Gatto
Computational Biology and Bioinformatics, UCLouvainlaurent.gatto@uclouvain.be
12 July 2025
Source:vignettes/sager.Rmd
sager.RmdIntroduction
The sager package
Sage is a new
cross-platform, extremely performant, open source proteomics search
engine Michael Lazear. It uses
mzML files as input, is parameterised by a json file
and is executed from the command line. In addition to peptide
identification, sage also includes a variety of advanced features such
as retention time prediction and quantification (both isobaric &
LFQ). It produces two files: results.sage.tsv with the
identification results and, when configured to quantify features,
quant.tsv.
The sager package uses these two files as input. It
facilitates their import into established Bioconductor classes:
Identification results are parsed and imported as PSMatch::PSM() objects with
sagePSM().Quantitation (and identification) results are parsed, merged and imported as QFeatures::QFeatures() objects with
sageQFeatures().Sage results can also be integrated with a Spectra::Spectra() instance (holding the raw data) into a MsExperiment::MsExperiment() object, as documented in this document.
The goal of the sager package can thus be summarised as
a way to leverage the existing R for Mass Spectrometry
and Bioconductor infrastructure
to analyse sage results.
Installation instructions
To install sager and its dependencies, you’ll need the
BiocManager package, that can be installed from CRAN
(unless you already have it):
if (!requireNamespace("BiocManager"))
install.packages("BiocManager")Note that sager is under constant development, and thus
will depend on some under-development dependencies, that haven’t made it
into the stable releases yet. Here are the instructions to install
these:
To install the devel version of PSMatch:
BiocManager::install("RforMassSpectrometry/PSMatch")To install sager and its dependencies, you can run the
following command:
BiocManager::install("UCLouvain-CBIO/sager")Analysing sage results
Example data
library(sager)The sager package provides example identification and
quantitation (procuced by sage) and the raw data
(mzML files) that were used the generate the former.
sagerAvailableData()
#> quant id mzml
#> TRUE TRUE TRUEData can be added with the sagerAddData() function, that
avoid downloading data files if they are already available in the
package’s local cache directory:
sagerAddData()
#> 'quant' already available.
#> 'id' already available.
#> 'mzml' already available.For details, including updating local data and their provenance,
please see the ?sagerData manual page.
Identification data
As noted above, identification data is handled by the PSMatch package. This section only provides a very short example of how to use it. For more details, see the package’s website and vignettes.
library(PSMatch)
psm <- sagePSM(sagerIdData())
psm
#> PSM with 977 rows and 34 columns.
#> names(34): peptide proteins ... protein_fdr ms1_intensityHere we briefly visualise the sage_discriminant_score
and spectrum FDR densities for the forward and decoy/reverse hits:
library(ggplot2)
data.frame(psm) |>
ggplot(aes(x = sage_discriminant_score,
colour = label)) +
geom_density()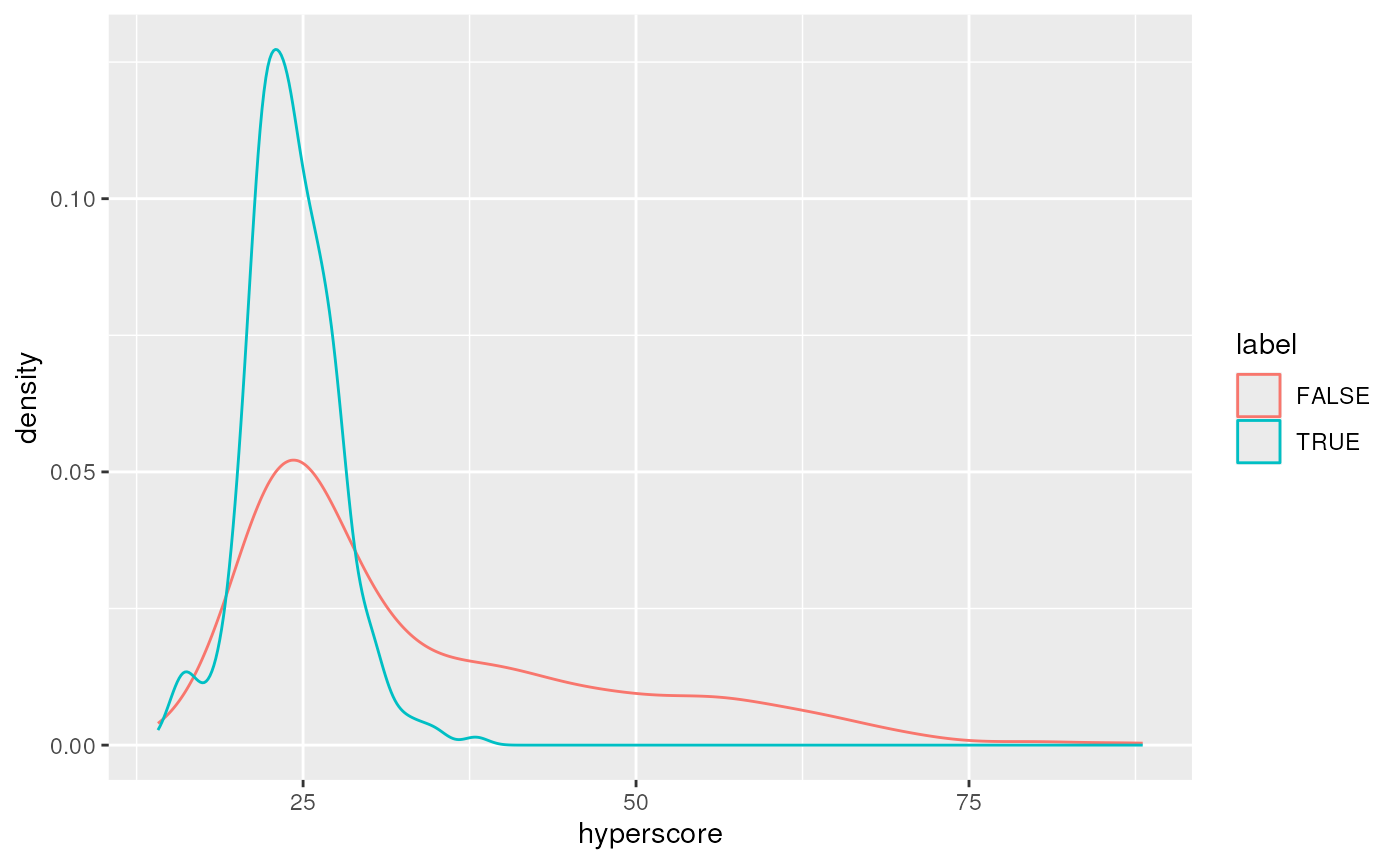
data.frame(psm) |>
ggplot(aes(x = spectrum_fdr,
colour = label)) +
geom_density()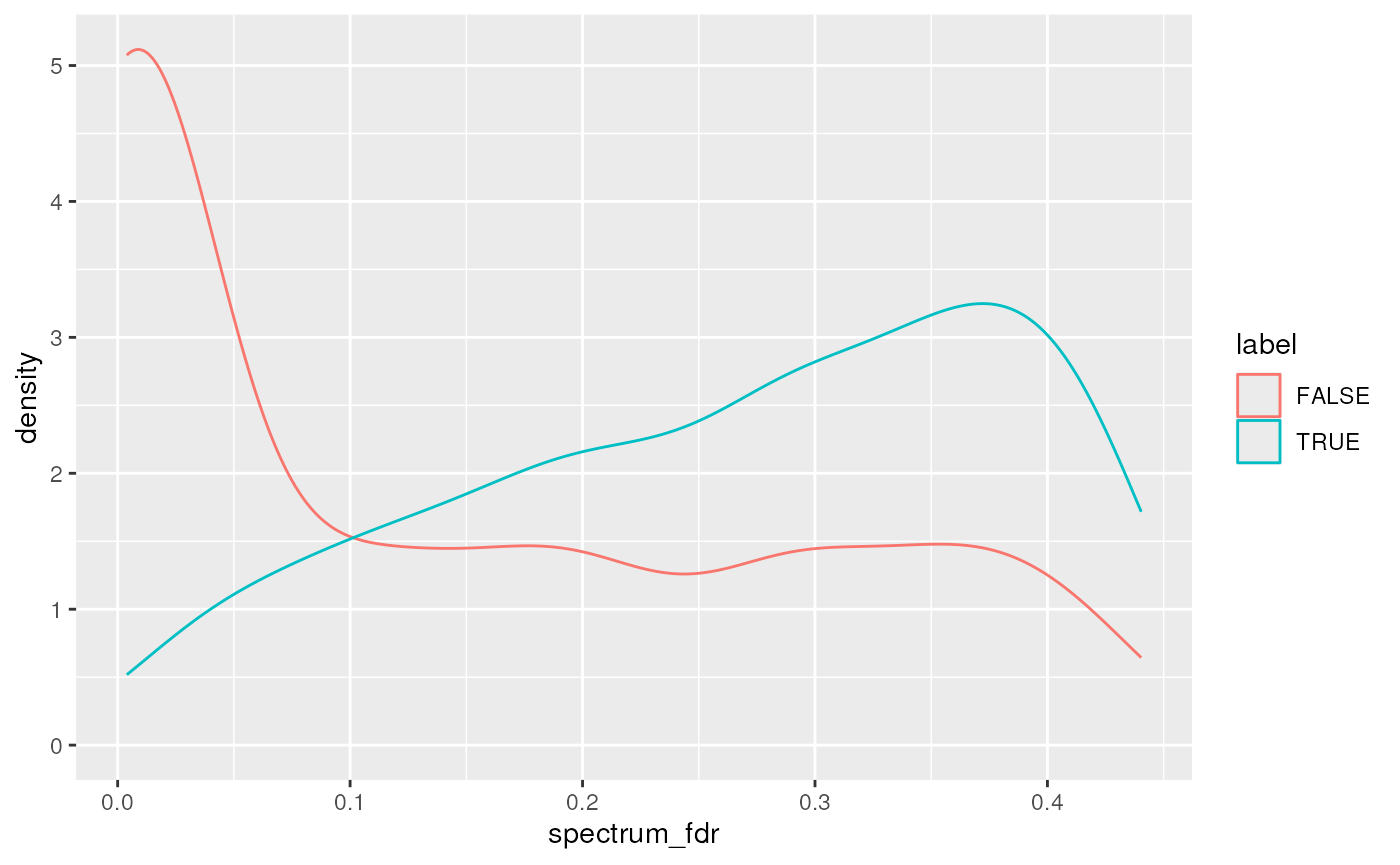
Below, we filter the PSMs removing decoy hits, PSMs of rank > 1 (none in the small testing data), shared peptides (none in the small testing data) and those that have a spectrum FDR below 0.05:
psm <- filterPSMs(psm) |>
filterPsmFdr()
#> Starting with 977 PSMs:
#> Removed 298 decoy hits.
#> Removed 0 PSMs with rank > 1.
#> Removed 0 shared peptides.
#> 679 PSMs left.This leaves us with 679 PSMs matched against 481 scans.
psm
#> PSM with 679 rows and 34 columns.
#> names(34): peptide proteins ... protein_fdr ms1_intensityQuantitative data
As noted above, quantitation data is handled by the QFeatures package. This section only provides a very short example of how to use it. For more details, see the package’s website and vignettes.
We will also make use of some function from the scp package.
The quantitation data has been produced from running
sage on three raw data files. These three files can
correspond to two different experimental designs:
The three acquisitions correspond to three fractions of the same set of 11 multiplexed samples. In this case, that we’ll call the Multiple fractions for the same set of samples, we end up with a single quantitation matrix with 11 columns and row containing the features from all files.
The three acquisitions correspond to single acquisitions from 3 different sets of 11 samples. In this case, that we’ll call the Different sets of samples per acquisition, we end up with three quantitation matrices, each with 11 columns and rows containing the features from the respective files.
Both sitations are illustrated below using the
sageQFeatures() function , and a differenciated by the
value of the splitBy argument. Note that below, the
byQuant argument is set to accomodate the old sage default
header; this byQuant argument wouldn’t need to be set
explicitly for newer output files.
Multiple fractions for the same set of samples
Let’s read the data in, specifying that the tables should not be split into different quantitative assays.
qf1 <- sageQFeatures(sagerQuantData(),
sagerIdData(),
byQuant = c("file", "scannr"),
splitBy = NULL)
#> Warning in .checkWarnEcol(quantCols, ecol): 'ecol' is deprecated, use
#> 'quantCols' instead.
qf1
#> An instance of class QFeatures (type: bulk) with 1 set:
#>
#> [1] sage: SummarizedExperiment with 977 rows and 11 columnsThe piped commands below implement the following worflow:
- Filter decoy features (i.e. those with a label of -1).
- Only keep features of rank 1.
- Keep features that have a spectrum FDR smaller than 0.05.
- Replace 0s by
NA, to make missing values explicit. - Log-transform quantitative values.
- Normalise data using median centring.
- Aggregate features into protein-level quantities by computing the median and ignoring missing values.
qf1 |>
filterFeatures(~ label > 0) |> ## 1
filterFeatures(~ rank == 1) |> ## 2
filterFeatures(~ spectrum_fdr < 0.05) |> ## 3
zeroIsNA(1) |> ## 4
logTransform(i = 1, name = "log_sage") |> ## 5
normalize(i = "log_sage", ## 6
name = "norm_sage",
method = "center.median") |>
aggregateFeatures(i = "norm_sage", ## 7
name = "proteins",
fcol = "proteins",
fun = colMedians,
na.rm = TRUE) -> qf1
#> 'label' found in 1 out of 1 assay(s).
#> 'rank' found in 1 out of 1 assay(s).
#> 'spectrum_fdr' found in 1 out of 1 assay(s).
#> Your quantitative data contain missing values. Please read the relevant
#> section(s) in the aggregateFeatures manual page regarding the effects
#> of missing values on data aggregation.
#> Aggregated: 1/1The new QFeatures object contains 4 assays:
qf1
#> An instance of class QFeatures (type: bulk) with 4 sets:
#>
#> [1] sage: SummarizedExperiment with 309 rows and 11 columns
#> [2] log_sage: SummarizedExperiment with 309 rows and 11 columns
#> [3] norm_sage: SummarizedExperiment with 309 rows and 11 columns
#> [4] proteins: SummarizedExperiment with 297 rows and 11 columnsThe pipeline can then be visualised as shown below:
plot(qf1)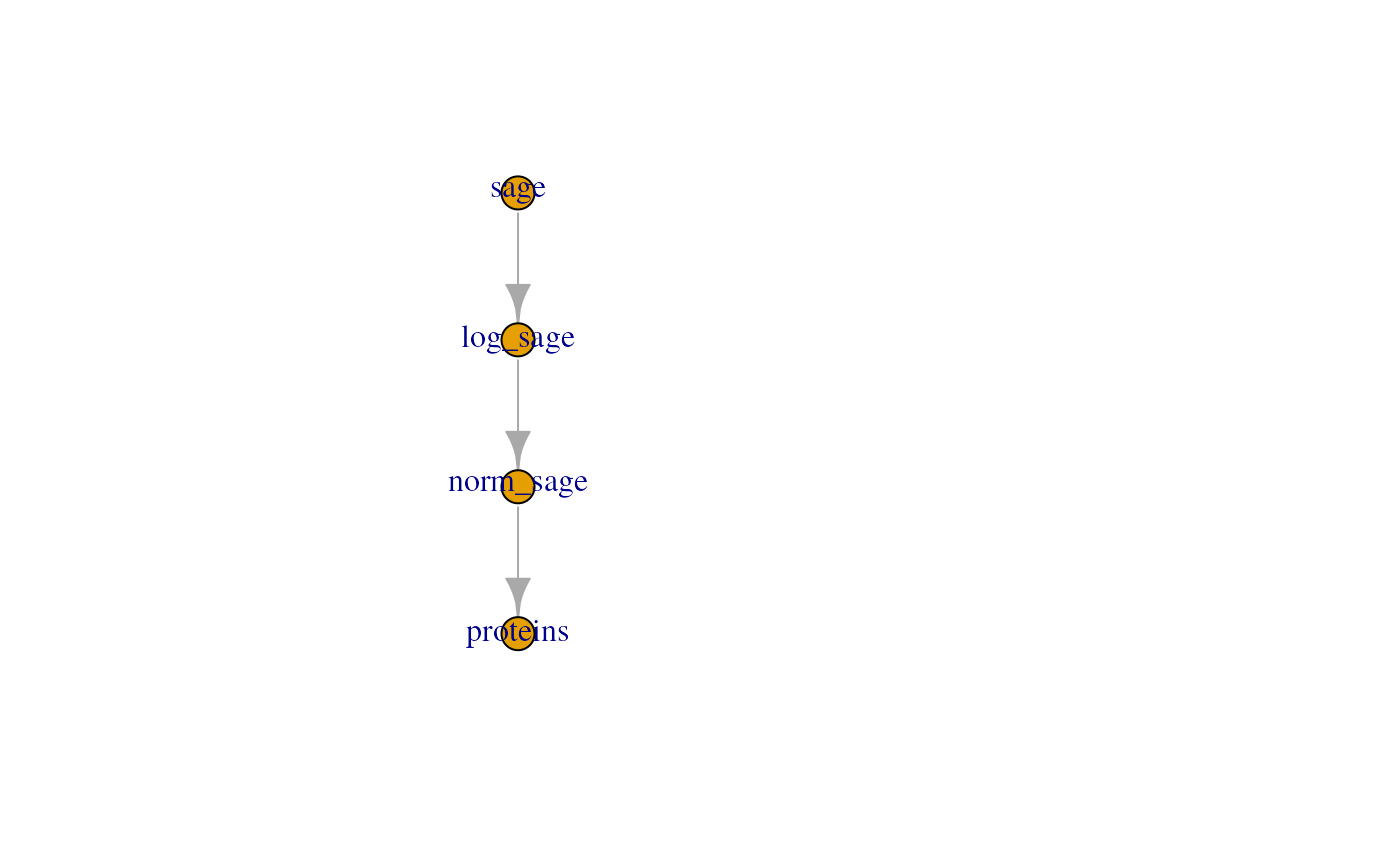
Different sets of samples per acquisition
In this second example, the quantitative data are automatically split based on the mzML files.
qf <- sageQFeatures(sagerQuantData(), sagerIdData(),
byQuant = c("file", "scannr"))
#> Warning in .checkWarnEcol(quantCols, ecol): 'ecol' is deprecated, use
#> 'quantCols' instead.
#> Warning in .checkWarnEcol(quantCols, ecol): 'ecol' is deprecated, use
#> 'quantCols' instead.
#> Warning in .checkWarnEcol(quantCols, ecol): 'ecol' is deprecated, use
#> 'quantCols' instead.
qf
#> An instance of class QFeatures (type: bulk) with 3 sets:
#>
#> [1] subset_dq_00084_11cell_90min_hrMS2_A5.mzML: SummarizedExperiment with 288 rows and 11 columns
#> [2] subset_dq_00086_11cell_90min_hrMS2_A9.mzML: SummarizedExperiment with 353 rows and 11 columns
#> [3] subset_dq_00087_11cell_90min_hrMS2_A11.mzML: SummarizedExperiment with 336 rows and 11 columnsBefore processing the data, let’s annotate it. The
renameqf() helper function will automate come of the file
renaming. The annotation will be composed of the file name of origin
(filename), the TMT tag (tmt_tag), and and
acquisition identifier (acquisition).
renameqf <- function(x) sub("\\.mzML", "", sub("^.+hrMS2_", "", x))
qf$filename <- rep(names(qf), each = 11)
qf$tmt_tag <- rep(paste0("tmt_", 1:11), length(qf))
qf$acquisition <- renameqf(qf$filename)
names(qf) <- paste0("psm", renameqf(names(qf)))Below, we update the assay and sample names.
qf <- renamePrimary(qf, paste(qf$acquisition, qf$tmt_tag, sep = "."))
colnames(qf) <- CharacterList(lapply(colnames(qf), renameqf))
colData(qf)
#> DataFrame with 33 rows and 3 columns
#> filename tmt_tag acquisition
#> <character> <character> <character>
#> A5.tmt_1 subset_dq_... tmt_1 A5
#> A5.tmt_2 subset_dq_... tmt_2 A5
#> A5.tmt_3 subset_dq_... tmt_3 A5
#> A5.tmt_4 subset_dq_... tmt_4 A5
#> A5.tmt_5 subset_dq_... tmt_5 A5
#> ... ... ... ...
#> A11.tmt_7 subset_dq_... tmt_7 A11
#> A11.tmt_8 subset_dq_... tmt_8 A11
#> A11.tmt_9 subset_dq_... tmt_9 A11
#> A11.tmt_10 subset_dq_... tmt_10 A11
#> A11.tmt_11 subset_dq_... tmt_11 A11
qf
#> An instance of class QFeatures (type: bulk) with 3 sets:
#>
#> [1] psmA5: SummarizedExperiment with 288 rows and 11 columns
#> [2] psmA9: SummarizedExperiment with 353 rows and 11 columns
#> [3] psmA11: SummarizedExperiment with 336 rows and 11 columnsThe piped commands below implement the following worflow:
- Filter decoy features (i.e. those with a label of -1) in all assays.
- Only keep features of rank 1 in all assays.
- Keep features that have a spectrum FDR smaller than 0.05 in all assays.
- Replace 0s by
NAin all assays, to make missing values explicit. - Log-transform quantitative values - three new assays are created from the three initial ones and named with the “log_” prefix.
- Aggregate each PSMs into peptide-level quantities by computing the median and ignoring missing values. The new assays names are defined as ‘peptide’ followed by the orifinal assay identifier.
- Join the 3 peptide assays into a new assay that will contain the 33 samples. Missing values are incorporated accordingly, when a peptide is observed in part of the sets.
- Normalise the joined peptide data using median centring.
- Aggregate the peptide-level quantities into protein by computing the median and ignoring missing values. The new assay names will be ‘protein’.
qf |>
filterFeatures(~ label > 0) |> ## 1
filterFeatures(~ rank == 1) |> ## 2
filterFeatures(~ spectrum_fdr < 0.05) |> ## 3
zeroIsNA(1:3) |> ## 4
logTransform(i = 1:3, ## 5
name = paste0("log_", names(qf))) |>
aggregateFeaturesOverAssays(i = 4:6, ## 6
fcol = "peptide",
name = sub("psm", "peptide", names(qf)),
fun = colMedians,
na.rm = TRUE) |>
joinAssays(i = 7:9, ## 7
name = "peptides") |>
normalize(i = 10, ## 8
name = "norm_peptides",
method = "center.median") |>
aggregateFeatures(i = "norm_peptides", ## 9
name = "proteins",
fcol = "proteins",
fun = colMedians,
na.rm = TRUE) -> qf
#> Warning in aggregateFeaturesOverAssays(logTransform(zeroIsNA(filterFeatures(filterFeatures(filterFeatures(qf, : 'aggregateFeaturesOverAssays' is deprecated.
#> Use 'aggregateFeatures' instead.
#> See help("Deprecated") and help("QFeatures-deprecated").
#> 'label' found in 3 out of 3 assay(s).
#> 'rank' found in 3 out of 3 assay(s).
#> 'spectrum_fdr' found in 3 out of 3 assay(s).
#> Aggregated: 1/3
#> Aggregated: 2/3
#> Aggregated: 3/3
#> Your quantitative data contain missing values. Please read the relevant
#> section(s) in the aggregateFeatures manual page regarding the effects
#> of missing values on data aggregation.
#> Aggregated: 1/1The final QFeatures object now contains 12 assays:
qf
#> An instance of class QFeatures (type: bulk) with 12 sets:
#>
#> [1] psmA5: SummarizedExperiment with 91 rows and 11 columns
#> [2] psmA9: SummarizedExperiment with 109 rows and 11 columns
#> [3] psmA11: SummarizedExperiment with 109 rows and 11 columns
#> ...
#> [10] peptides: SummarizedExperiment with 308 rows and 33 columns
#> [11] norm_peptides: SummarizedExperiment with 308 rows and 33 columns
#> [12] proteins: SummarizedExperiment with 297 rows and 33 columnsThe pipeline can then be visualised as shown below:
plot(qf)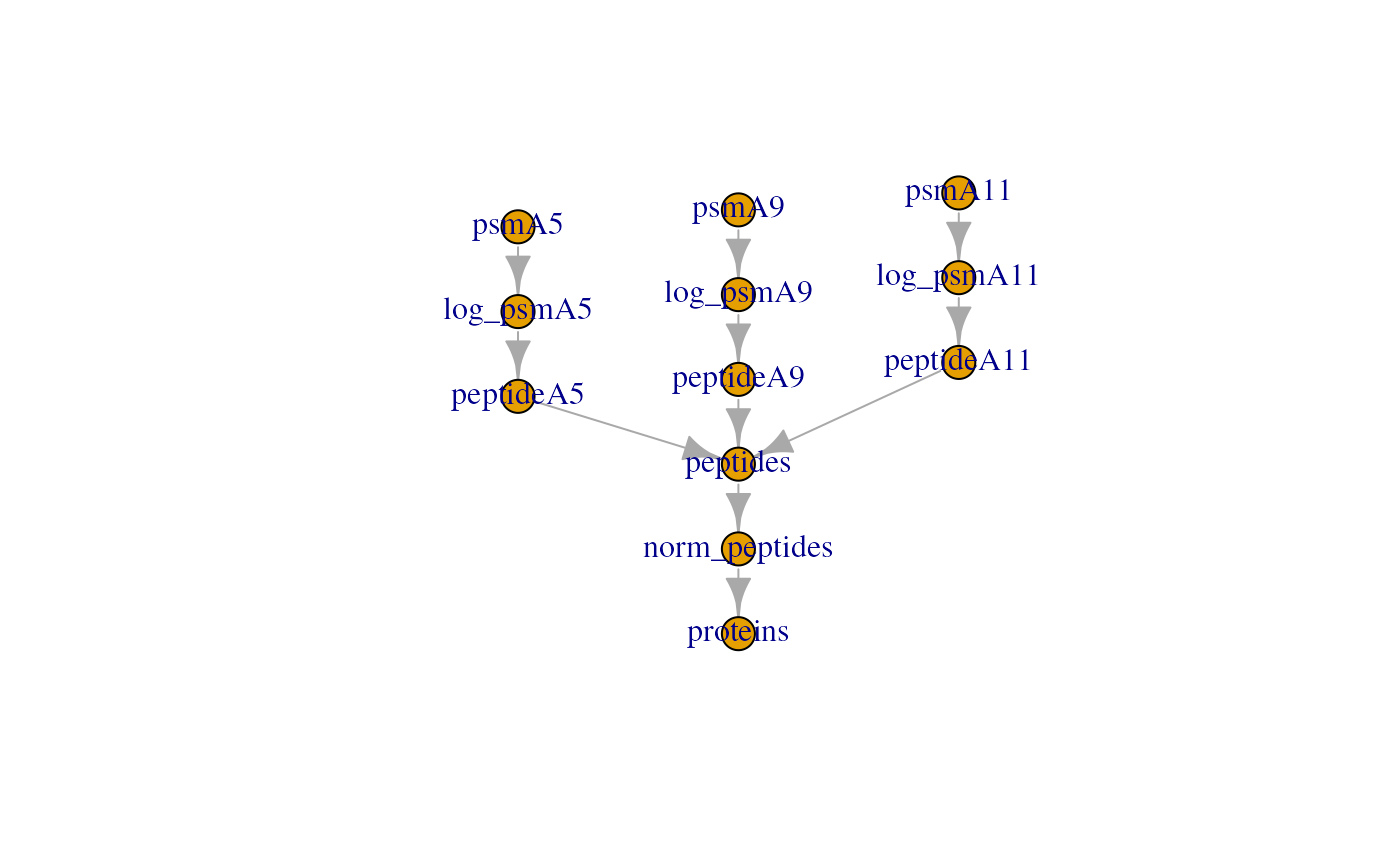
Raw data
We have seen above how to import and process identification and quantitation data produced by sage using standard R/Bioconductor tools. Our main goal is to integrate these with the raw MS data that was used to generate them.
Let’s start by importing these raw data into R as a
Spectra object. The three mzML files can be retrieved with
the sagerMzMLData() function.
library(Spectra)
sp <- Spectra(sagerMzMLData())
sp
#> MSn data (Spectra) with 598 spectra in a MsBackendMzR backend:
#> msLevel rtime scanIndex
#> <integer> <numeric> <integer>
#> 1 2 279.184 1
#> 2 2 731.098 2
#> 3 2 736.768 3
#> 4 2 863.610 4
#> 5 2 866.034 5
#> ... ... ... ...
#> 594 2 5155.97 203
#> 595 2 5163.48 204
#> 596 2 5178.80 205
#> 597 2 5179.03 206
#> 598 2 5249.68 207
#> ... 34 more variables/columns.
#>
#> file(s):
#> subset_dq_00084_11cell_90min_hrMS2_A5.mzML
#> subset_dq_00086_11cell_90min_hrMS2_A9.mzML
#> subset_dq_00087_11cell_90min_hrMS2_A11.mzMLCombining raw, quantitation and identification data
Defining keys
We can now create dedicates keys to identify features in the
different data produced above. Let’s start with the spectra within the
sp object. Later, we will create a similar key in the
QFeatures and PSM objects generated above.
The goal of these keys will be to identify matching features across
data types, such as for example to match de MS spectra to the PSMs and
peptides or proteins. These different data types can be stored together
in an MsExperiment object, and matched through one or
multiple keys.
We can add a key (by default, names .KEY that will
identify a feature/scan by concatenating the scan number and the file in
which that scan was acquired.
sp$filename <- basename(dataOrigin(sp))
sp <- addKey(sp, vars = c("filename", "spectrumId"))
head(sp$.KEY)
#> [1] "subset_dq_00084_11cell_90min_hrMS2_A5.mzML.controllerType=0 controllerNumber=1 scan=1004"
#> [2] "subset_dq_00084_11cell_90min_hrMS2_A5.mzML.controllerType=0 controllerNumber=1 scan=4181"
#> [3] "subset_dq_00084_11cell_90min_hrMS2_A5.mzML.controllerType=0 controllerNumber=1 scan=4224"
#> [4] "subset_dq_00084_11cell_90min_hrMS2_A5.mzML.controllerType=0 controllerNumber=1 scan=5124"
#> [5] "subset_dq_00084_11cell_90min_hrMS2_A5.mzML.controllerType=0 controllerNumber=1 scan=5144"
#> [6] "subset_dq_00084_11cell_90min_hrMS2_A5.mzML.controllerType=0 controllerNumber=1 scan=5517"Let’s do the same of the PSM object created above:
psm <- addKey(psm, vars = c("filename", "scannr"))
head(psm$.KEY)
#> [1] "subset_dq_00084_11cell_90min_hrMS2_A5.mzML.controllerType=0 controllerNumber=1 scan=31852"
#> [2] "subset_dq_00087_11cell_90min_hrMS2_A11.mzML.controllerType=0 controllerNumber=1 scan=31961"
#> [3] "subset_dq_00087_11cell_90min_hrMS2_A11.mzML.controllerType=0 controllerNumber=1 scan=16197"
#> [4] "subset_dq_00087_11cell_90min_hrMS2_A11.mzML.controllerType=0 controllerNumber=1 scan=32666"
#> [5] "subset_dq_00086_11cell_90min_hrMS2_A9.mzML.controllerType=0 controllerNumber=1 scan=22318"
#> [6] "subset_dq_00086_11cell_90min_hrMS2_A9.mzML.controllerType=0 controllerNumber=1 scan=11726"And finally, with the QFeatures object.
Running addKey on a QFeatures object will
only add a key to assays that do have the relevant variables:
sapply(rowData(qf), function(x) ".KEY" %in% names(x))
#> psmA5 psmA9 psmA11 log_psmA5 log_psmA9
#> TRUE TRUE TRUE TRUE TRUE
#> log_psmA11 peptideA5 peptideA9 peptideA11 peptides
#> TRUE TRUE FALSE TRUE FALSE
#> norm_peptides proteins
#> FALSE FALSE
head(unname(rowData(qf[["psmA5"]])$.KEY))
#> [1] "subset_dq_00084_11cell_90min_hrMS2_A5.mzML.controllerType=0 controllerNumber=1 scan=10460"
#> [2] "subset_dq_00084_11cell_90min_hrMS2_A5.mzML.controllerType=0 controllerNumber=1 scan=10530"
#> [3] "subset_dq_00084_11cell_90min_hrMS2_A5.mzML.controllerType=0 controllerNumber=1 scan=10648"
#> [4] "subset_dq_00084_11cell_90min_hrMS2_A5.mzML.controllerType=0 controllerNumber=1 scan=10803"
#> [5] "subset_dq_00084_11cell_90min_hrMS2_A5.mzML.controllerType=0 controllerNumber=1 scan=11681"
#> [6] "subset_dq_00084_11cell_90min_hrMS2_A5.mzML.controllerType=0 controllerNumber=1 scan=11785"Let’s now bundle these three types of data together into and
MsExperiment object:
library(MsExperiment)
#> Loading required package: ProtGenerics
#>
#> Attaching package: 'ProtGenerics'
#> The following object is masked from 'package:stats':
#>
#> smooth
mse <- MsExperiment()
spectra(mse) <- sp
qdata(mse) <- qf
otherData(mse)$PSM <- psm
mse
#> Object of class MsExperiment
#> Spectra: MS2 (598)
#> QFeatures: 12 assay(s)
#> Other data: PSMSearching for features across data types
Each data element mse is referenced by the same key. We
can now query for such keys direcly on the MsExperiment
object, that will percolate the request to its components.
k <- c("subset_dq_00084_11cell_90min_hrMS2_A5.mzML.controllerType=0 controllerNumber=1 scan=31852",
"subset_dq_00087_11cell_90min_hrMS2_A11.mzML.controllerType=0 controllerNumber=1 scan=32666")
filterKey(mse, k)
#> harmonizing input:
#> removing 132 sampleMap rows not in names(experiments)
#> removing 11 colData rownames not in sampleMap 'primary'
#> Object of class MsExperiment
#> Spectra: MS2 (2)
#> QFeatures: 6 assay(s)
#> Other data: PSMIt is however not convenient to search an arbitrary key. The more useful usecase would be to look for a protein of interest, for example, and then identify the features across other data types using the relevant key(s).
Let’s imagine that protein DNLI3_HUMAN is of interest to us.
It is referenced as "sp|P49916|DNLI3_HUMAN" in our data.
The dropEmptyAssay() simply drops assays that didn’t
reference the protein of interest - it is used to simplify the output
here.
qdata(mse)["sp|P49916|DNLI3_HUMAN", , ] |>
dropEmptyAssays()
#> Warning: 'experiments' dropped; see 'drops()'
#> harmonizing input:
#> removing 66 sampleMap rows not in names(experiments)
#> An instance of class QFeatures (type: bulk) with 6 sets:
#>
#> [1] psmA5: SummarizedExperiment with 1 rows and 11 columns
#> [2] log_psmA5: SummarizedExperiment with 1 rows and 11 columns
#> [3] peptideA5: SummarizedExperiment with 1 rows and 11 columns
#> [4] peptides: SummarizedExperiment with 1 rows and 33 columns
#> [5] norm_peptides: SummarizedExperiment with 1 rows and 33 columns
#> [6] proteins: SummarizedExperiment with 1 rows and 33 columnsThese are features that we might be interested in tracking across all
data using their key… which we can easily retrieve with the
getKey() function:
qdata(mse)["sp|P49916|DNLI3_HUMAN", , ] |>
dropEmptyAssays() |>
getKey()
#> Warning: 'experiments' dropped; see 'drops()'
#> List of length 3
#> names(3): psmA5 log_psmA5 peptideA5Given that getKey() is run on a QFeatures
object, it returns the keys of all assays. Let’s extract the unique keys
as a character:
my_key <- qdata(mse)["sp|P49916|DNLI3_HUMAN", , ] |>
dropEmptyAssays() |>
getKey() |>
unlist() |>
unique()
#> Warning: 'experiments' dropped; see 'drops()'
my_key
#> [1] "subset_dq_00084_11cell_90min_hrMS2_A5.mzML.controllerType=0 controllerNumber=1 scan=17928"And now use mykey to subset the different component of
the MsExperiment object:
my_mse <- filterKey(mse, my_key)
#> harmonizing input:
#> removing 165 sampleMap rows not in names(experiments)
#> removing 22 colData rownames not in sampleMap 'primary'
my_mse
#> Object of class MsExperiment
#> Spectra: MS2 (1)
#> QFeatures: 3 assay(s)
#> Other data: PSMFrom the above, we can see that DNLI3_HUMAN was identified and quantified by a single peptides, that has the following quantitation profile acorss the 11 samples…
assay(qdata(my_mse)[[3]])
#> A5.tmt_1 A5.tmt_2 A5.tmt_3 A5.tmt_4 A5.tmt_5
#> [+229.1629]-SATNLPQLK[+229.1629] 18.48759 19.64292 NaN NaN 18.4555
#> A5.tmt_6 A5.tmt_7 A5.tmt_8 A5.tmt_9 A5.tmt_10
#> [+229.1629]-SATNLPQLK[+229.1629] NaN 20.28052 18.19301 NaN 18.82892
#> A5.tmt_11
#> [+229.1629]-SATNLPQLK[+229.1629] NaN… and that that peptides was matched by a single spectrum, shown below:
plotSpectra(spectra(my_mse))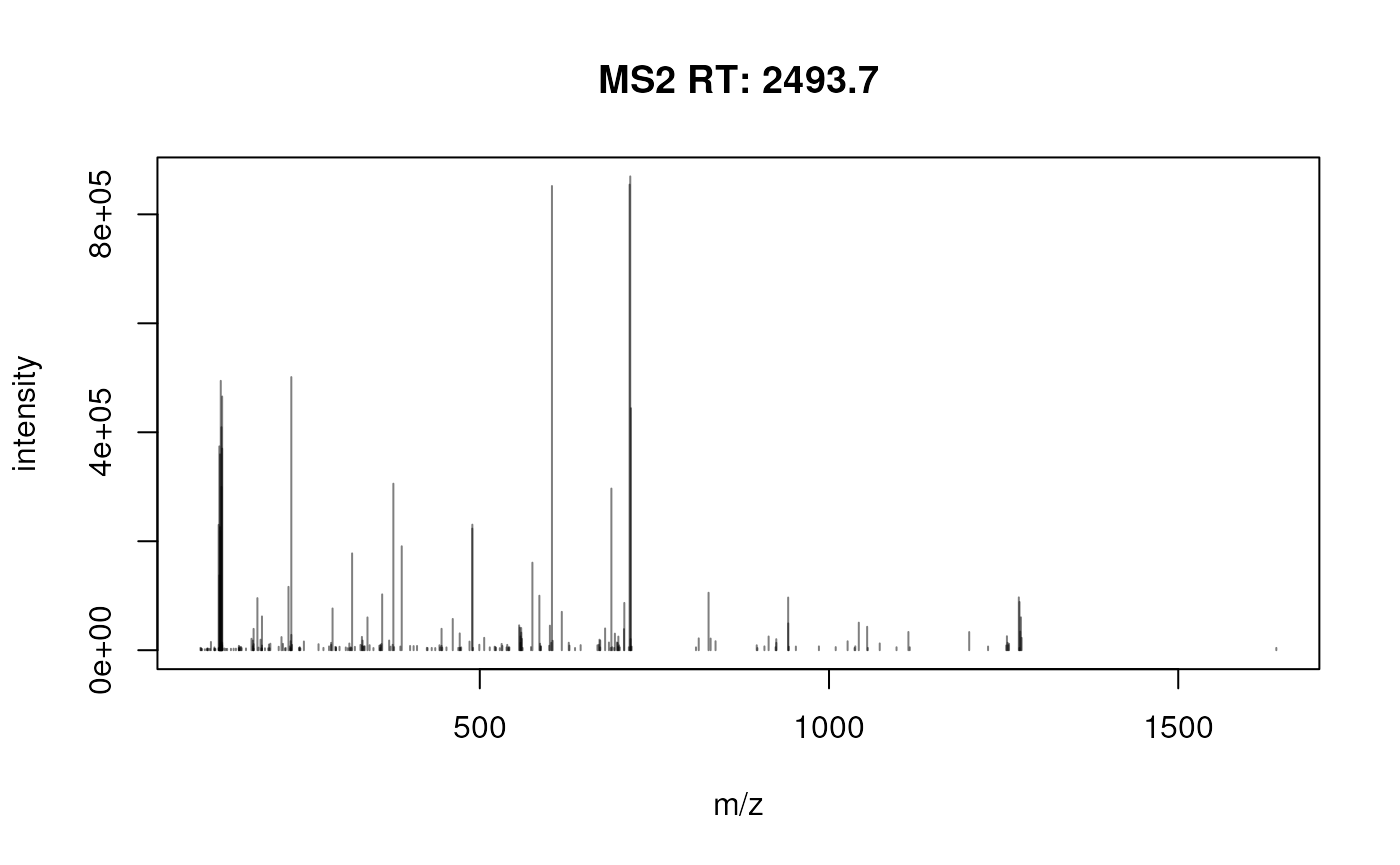
Misc
Getting help
Please open an issue on the package’s Github repository.
Session information
#> R version 4.5.1 (2025-06-13)
#> Platform: x86_64-pc-linux-gnu
#> Running under: Ubuntu 24.04.2 LTS
#>
#> Matrix products: default
#> BLAS: /usr/lib/x86_64-linux-gnu/openblas-pthread/libblas.so.3
#> LAPACK: /usr/lib/x86_64-linux-gnu/openblas-pthread/libopenblasp-r0.3.26.so; LAPACK version 3.12.0
#>
#> locale:
#> [1] LC_CTYPE=en_US.UTF-8 LC_NUMERIC=C
#> [3] LC_TIME=en_US.UTF-8 LC_COLLATE=en_US.UTF-8
#> [5] LC_MONETARY=en_US.UTF-8 LC_MESSAGES=en_US.UTF-8
#> [7] LC_PAPER=en_US.UTF-8 LC_NAME=C
#> [9] LC_ADDRESS=C LC_TELEPHONE=C
#> [11] LC_MEASUREMENT=en_US.UTF-8 LC_IDENTIFICATION=C
#>
#> time zone: UTC
#> tzcode source: system (glibc)
#>
#> attached base packages:
#> [1] stats4 stats graphics grDevices utils datasets methods
#> [8] base
#>
#> other attached packages:
#> [1] MsExperiment_1.11.1 ProtGenerics_1.41.0
#> [3] Spectra_1.19.2 BiocParallel_1.43.4
#> [5] scp_1.19.2 QFeatures_1.19.3
#> [7] MultiAssayExperiment_1.35.3 SummarizedExperiment_1.39.1
#> [9] Biobase_2.69.0 GenomicRanges_1.61.1
#> [11] Seqinfo_0.99.1 IRanges_2.43.0
#> [13] MatrixGenerics_1.21.0 matrixStats_1.5.0
#> [15] ggplot2_3.5.2 PSMatch_1.13.2
#> [17] S4Vectors_0.47.0 BiocGenerics_0.55.0
#> [19] generics_0.1.4 sager_0.3.3
#> [21] BiocStyle_2.37.0
#>
#> loaded via a namespace (and not attached):
#> [1] DBI_1.2.3 httr2_1.1.2
#> [3] fdrtool_1.2.18 rlang_1.1.6
#> [5] magrittr_2.0.3 clue_0.3-66
#> [7] compiler_4.5.1 RSQLite_2.4.1
#> [9] systemfonts_1.2.3 vctrs_0.6.5
#> [11] reshape2_1.4.4 nipals_1.0
#> [13] stringr_1.5.1 pkgconfig_2.0.3
#> [15] MetaboCoreUtils_1.17.1 crayon_1.5.3
#> [17] fastmap_1.2.0 dbplyr_2.5.0
#> [19] XVector_0.49.0 labeling_0.4.3
#> [21] rmarkdown_2.29 ragg_1.4.0
#> [23] purrr_1.1.0 bit_4.6.0
#> [25] xfun_0.52 cachem_1.1.0
#> [27] jsonlite_2.0.0 blob_1.2.4
#> [29] DelayedArray_0.35.2 parallel_4.5.1
#> [31] cluster_2.1.8.1 R6_2.6.1
#> [33] bslib_0.9.0 stringi_1.8.7
#> [35] RColorBrewer_1.1-3 jquerylib_0.1.4
#> [37] Rcpp_1.1.0 bookdown_0.43
#> [39] knitr_1.50 BiocBaseUtils_1.11.0
#> [41] Matrix_1.7-3 igraph_2.1.4
#> [43] tidyselect_1.2.1 abind_1.4-8
#> [45] yaml_2.3.10 codetools_0.2-20
#> [47] curl_6.4.0 lattice_0.22-7
#> [49] tibble_3.3.0 plyr_1.8.9
#> [51] withr_3.0.2 evaluate_1.0.4
#> [53] desc_1.4.3 BiocFileCache_2.99.5
#> [55] IHW_1.37.0 pillar_1.11.0
#> [57] BiocManager_1.30.26 filelock_1.0.3
#> [59] lpsymphony_1.37.0 ncdf4_1.24
#> [61] scales_1.4.0 glue_1.8.0
#> [63] slam_0.1-55 metapod_1.17.0
#> [65] lazyeval_0.2.2 tools_4.5.1
#> [67] mzR_2.43.0 fs_1.6.6
#> [69] grid_4.5.1 tidyr_1.3.1
#> [71] MsCoreUtils_1.21.0 SingleCellExperiment_1.31.1
#> [73] cli_3.6.5 rappdirs_0.3.3
#> [75] textshaping_1.0.1 S4Arrays_1.9.1
#> [77] dplyr_1.1.4 AnnotationFilter_1.33.0
#> [79] gtable_0.3.6 sass_0.4.10
#> [81] digest_0.6.37 SparseArray_1.9.0
#> [83] ggrepel_0.9.6 htmlwidgets_1.6.4
#> [85] farver_2.1.2 memoise_2.0.1
#> [87] htmltools_0.5.8.1 pkgdown_2.1.3.9000
#> [89] lifecycle_1.0.4 bit64_4.6.0-1
#> [91] MASS_7.3-65